Linear shafts, also referred to as bearing shafts, linear rods, or ground shafts, are precision ground metal rods with a hardened surface. They facilitate smooth and accurate linear motion in countless applications. From industrial machinery to everyday household items, these seemingly simple components play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
What are Linear Shafts?
Linear shafts are cylindrical rods designed to provide a smooth, low-friction surface for linear bearings to travel along. These precision-engineered components serve as the backbone of many linear motion systems, enabling controlled movement in a straight line. Typically manufactured from high-quality materials such as hardened steel or stainless steel, linear shafts are characterized by their exceptional straightness, roundness, and surface finish.
The primary function of linear shafts is to guide and support linear bearings, which in turn facilitate the movement of various mechanical components. This symbiotic relationship between shafts and bearings forms the foundation of numerous linear motion applications, ranging from simple sliding doors to complex industrial automation systems.
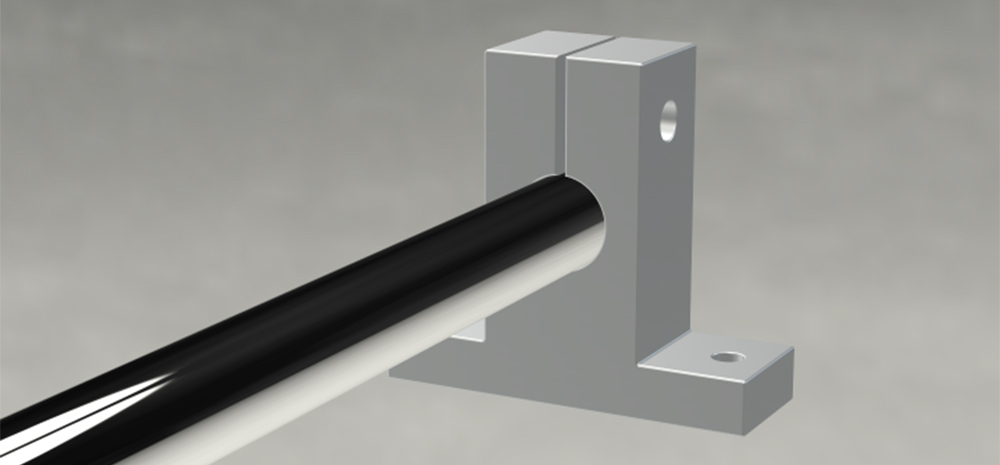
The Role of Linear Shafts
Linear shafts play a multifaceted role in mechanical systems, contributing to various aspects of performance and functionality:
Guidance
The primary function of linear shafts is to guide linear bearings along a precise path, ensuring smooth and controlled motion. This guidance is crucial for maintaining accuracy in positioning systems, manufacturing processes, and measurement equipment.
Load Support
Linear shafts bear the weight of the components mounted on the linear bearings, as well as any additional loads applied during operation. Their ability to withstand these forces without deflection or deformation is essential for system stability and performance.
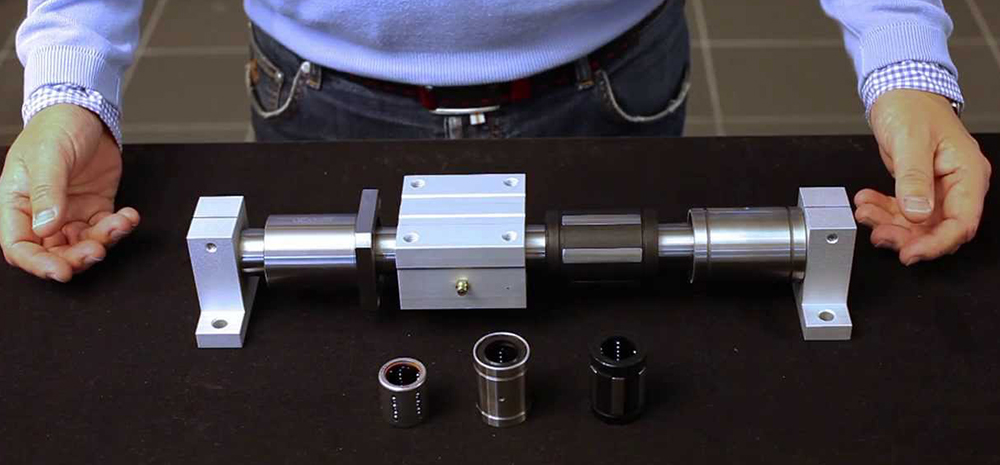

Precision
The high degree of straightness and roundness achieved in linear shafts contributes significantly to the overall precision of the motion system. This precision is critical in applications such as CNC machines, 3D printers, and scientific instruments.
Friction Reduction
The smooth surface finish of linear shafts, often combined with specialized coatings, helps minimize friction between the shaft and bearings. This reduction in friction leads to smoother motion, reduced wear, and improved energy efficiency. At the same time, lubrication and maintenance of the linear shafts are important measures to reduce wear.
Environmental Protection
In certain applications, linear shafts may serve as a barrier against contaminants, protecting internal components from dust, debris, or moisture. This is particularly important in harsh industrial environments or outdoor applications.
Structural Support
In some designs, linear shafts contribute to the overall structural integrity of the machine or device, providing additional rigidity and stability to the system.
Heat Dissipation
The metal construction of most linear shafts allows them to act as heat sinks, helping to dissipate thermal energy generated by moving components or external sources.
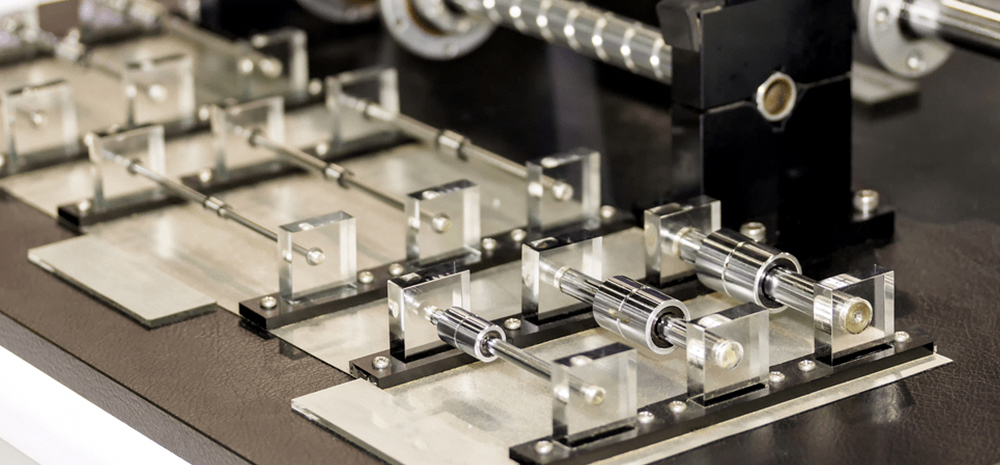
What Materials and Coatings Used in Linear Shafts?
The choice of materials and coatings for linear shafts significantly influences their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Let’s explore the most common options:
Materials:
Carbon Steel: Widely used for its strength and cost-effectiveness, carbon steel shafts are often induction hardened to improve wear resistance.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments or those requiring frequent cleaning.
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum shafts are suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Ceramic: Though less common, ceramic shafts provide exceptional hardness and wear resistance in specialized applications.
Composite Materials: Composite materials typically consist of carbon fibers that are held together by resins. Although they may not match the strength of metal shafts, their lightweight nature contributes to a decrease in energy requirements.
Coatings:
Anodizing: Anodizing is a protective surface coating process used mainly with aluminum products.
Chrome Plating: Chrome plating enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance while reducing friction.
Nickel Plating: It offers good corrosion resistance and can improve the shaft’s appearance.
Black Oxide: This process provides a thin, decorative coating that offers some corrosion protection.
PTFE (Teflon) Coating: It reduces friction and provides non-stick properties, beneficial in certain applications.
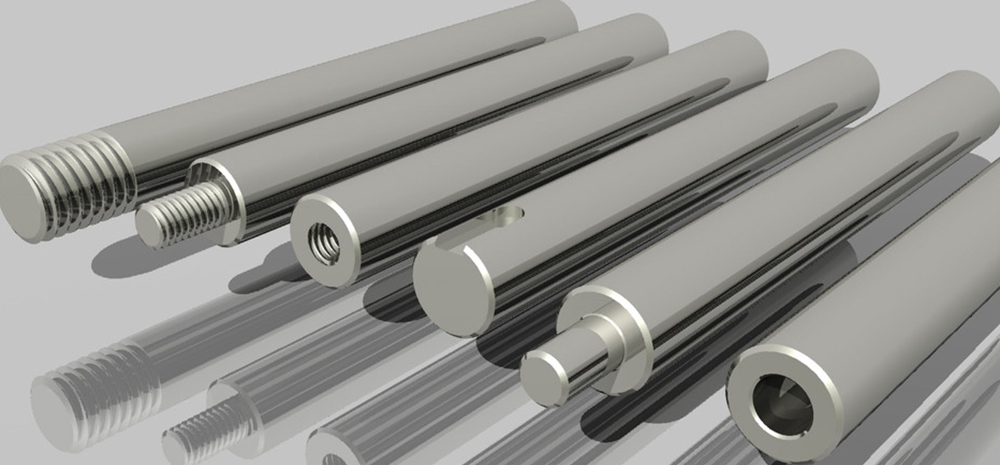
Types of Linear Motion Shafts
Linear shafts come in various configurations to accommodate different application requirements. Some common types include:
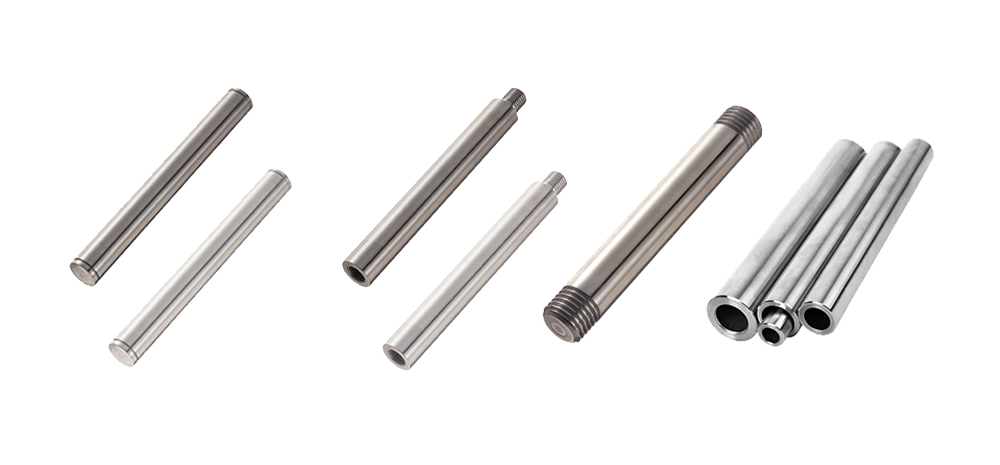
1. Solid Shafts:
– Fully solid cylindrical rods.
– Provide maximum rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
– Commonly used in applications requiring high precision and stiffness.
– Typically made from a single piece of material, usually hardened and ground steel.
2. Hollow Shafts:
– Cylindrical shafts with a hollow core.
– Lighter than solid shafts while maintaining good rigidity.
– Often used when weight reduction is important.
3. Tapped Shafts:
– Shafts with tapped holes at one or both ends.
– Internal threads allow to mount these shafts onto threaded studs.
– No shaft support is needed.
4. Threaded Shafts:
– Shafts with threaded holes at one or both ends.
– Do not need shaft support.
– Can mount the threaded rods into tapped holes.

Applications and Uses of Linear Shafts
The versatility of linear shafts has led to their widespread adoption across numerous industries. Some notable applications include:
Manufacturing and Automation
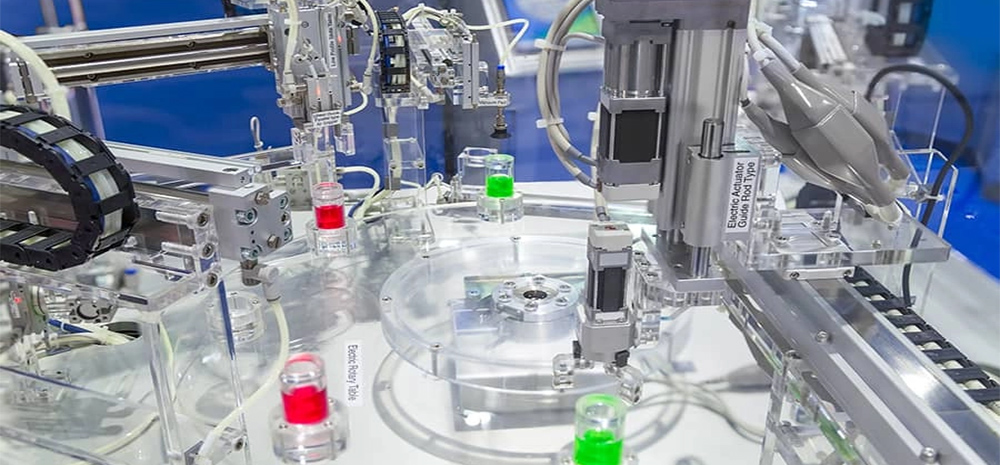
In industrial settings, linear shafts are extensively used in CNC machines, robotic systems, and automated assembly lines. They enable precise positioning and smooth movement of tools, workpieces, and robotic arms.

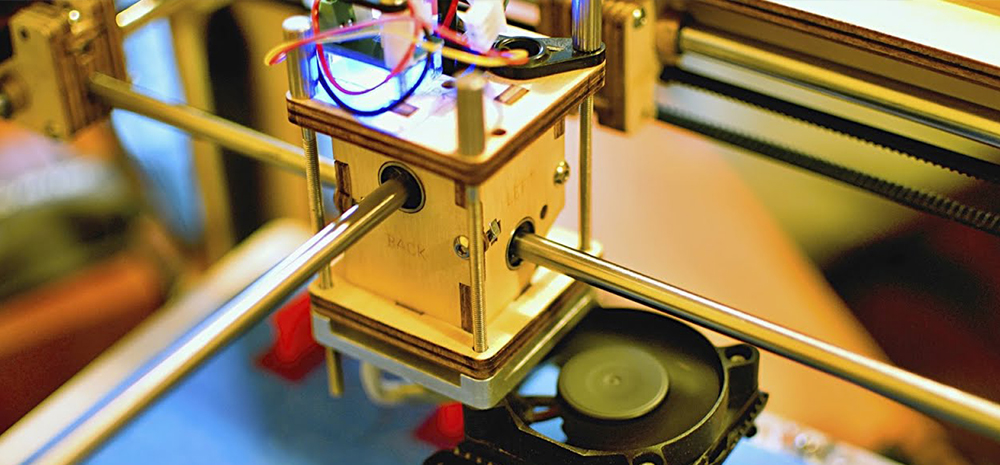
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
Linear shafts play a crucial role in 3D printers, guiding the print head with high precision to create intricate three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
From automated sample handling systems to medical imaging devices, linear shafts facilitate the precise movement of sensitive components in healthcare and scientific research applications.

Aerospace and Defense
In aircraft and military equipment, lightweight and high-performance linear shafts are used in various mechanisms, including control surfaces, satellite deployment mechanisms, aircraft landing gear, etc.
Automotive Industry
Linear shafts find applications in vehicle assembly lines, testing equipment, and even within vehicles themselves, such as in adjustable seating mechanisms.
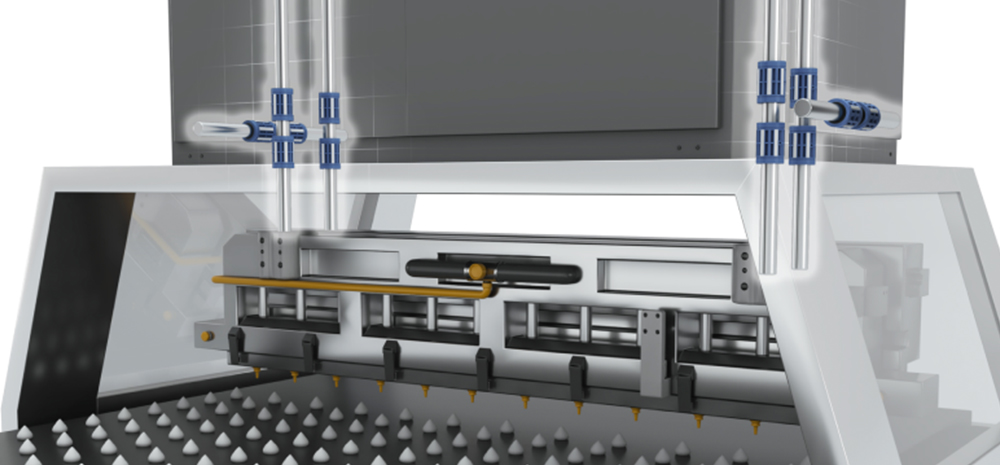
Packaging and Material Handling
Conveyor systems and packaging machinery rely on linear shafts to ensure smooth and efficient movement of products along production lines.
Key Considerations in Linear Shaft Selection
Choosing the appropriate linear shaft for a given application requires careful consideration of various factors. Engineers must evaluate:
Load Capacity: The ability of the shaft to withstand both static and dynamic loads without excessive deflection or deformation.
Straightness Tolerance: The degree of deviation from a perfectly straight line, which directly impacts the precision of the linear motion system.
Material Properties: Factors such as hardness, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability influence the shaft’s performance in different environments.
Surface Finish: The quality of the shaft’s surface affects friction, wear, and overall system efficiency.
Length and Diameter: These dimensions must be carefully selected to meet the specific requirements of the application while minimizing deflection.
Environmental Factors: Considerations such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances influence material and coating choices.
Cost and Availability: Balancing performance requirements with budgetary constraints and lead times is crucial for project success.
Summary
In modern mechanical systems, the linear shaft is a vital component, which plays a central role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of machinery. The main function of the linear shaft is to guide the direction of mechanical movement and ensure that the moving parts can move by the predetermined trajectory. This function is of vital importance in improving the efficiency, stability, and service life of mechanical systems.
FAR EAST TECH covers various linear motion components, including linear shafts, linear bearings, etc. For more detailed information, please refer to our Overseas Product Mall (https://www.fareasttech.com/ ).
